What is the Hydroponics System?
Hydroponic is a method of growing plants without soil. Instead, it involves using a nutrient-rich water solution to supply the necessary minerals and nutrients to the plants. The roots of the plants are submerged in the water solution or supported by an inert medium like perlite or clay pellets. This controlled environment allows for efficient water and nutrient uptake, resulting in faster plant growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based cultivation.
1. Deep Water Culture (DWC):
In DWC, also known as the "raft" or "pond" system, plants are suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution with their roots submerged in the water. The roots have access to oxygen through the use of air stones or diffusers. The plants float on Styrofoam boards or rafts, and the water is continuously oxygenated and recirculated through a pump and air stone system. DWC is a simple and effective system, suitable for growing leafy greens and herbs.
2. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT):
NFT is a popular hydroponic system where a thin film of nutrient solution flows continuously over the plant roots, which are supported by a sloped trough or tube. The roots are exposed to air, providing them with oxygen. The nutrient solution runs in a loop from a reservoir, over the roots, and back to the reservoir. NFT is best for fast-growing, shallow-rooted plants like lettuce, basil, and strawberries.
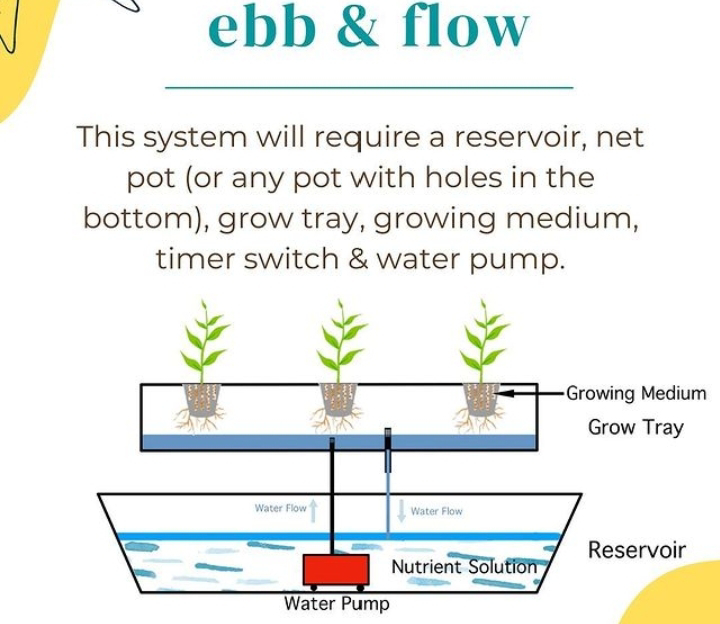
3. Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain):
In an Ebb and Flow system , plants are placed in trays or containers filled with a growing medium like gravel or clay pellets. The nutrient solution periodically floods the growing area, submerging the roots, and then drains back into the reservoir. This cycle ensures the roots receive both nutrients and oxygen. Ebb and Flow systems are versatile and suitable for a wide range of plants, from small herbs to large vegetables.
4. Drip System:
Drip systems use a network of tubing and emitters to deliver a controlled flow of nutrient solution directly to the base of each plant. The solution drips slowly onto the growing medium, allowing the roots to absorb nutrients and oxygen efficiently. Drip systems can be customized to suit various plant sizes and are commonly used for greenhouse farming.
5. Aeroponics:
Aeroponics is an advanced hydroponic system where plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with a fine nutrient solution. The roots are exposed to high levels of oxygen, resulting in rapid growth and increased nutrient absorption. Aeroponic systems are ideal for growing plants with delicate root structures, and they are often used in research and commercial setups.
6. Wick System:
The Wick System is one of the simplest hydroponic setups, requiring no pumps or electricity. In this passive system, a wick made of absorbent material, like cotton or felt, draws the nutrient solution from a reservoir to the plant's root zone. While it's straightforward and low-maintenance, the Wick system is best suited for small-scale or hobbyist gardening, and it may not be ideal for large, demanding crops.
Each hydroponic system has its pros and cons, and the choice depends on factors such as plant type, available space, budget, and grower's expertise.







No comments:
Post a Comment