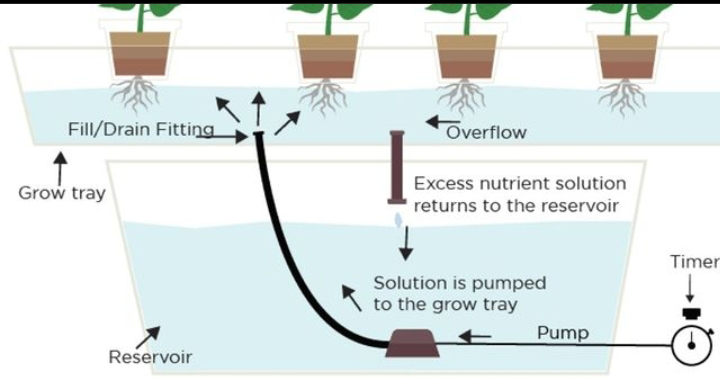
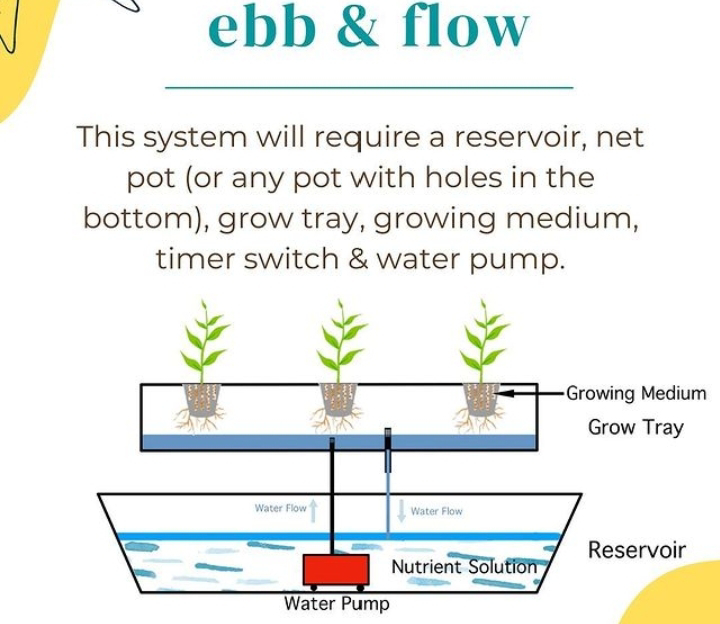
What is the Ebb and Flow system?
Its main components include a growing
tray, a reservoir, a submersible pump, and a timer.
1. Working: The system works by flooding the growing tray with nutrient-rich water from the reservoir. The submersible pump is activated by the timer, which fills the tray. Once the timer reaches a specific duration, it shuts off the pump, allowing the nutrient solution to drain back into the reservoir. This process repeats at regular intervals, creating a cycle of flooding and draining.
2. Benefits and Advantages:
- Efficient nutrient uptake: Plants have increased access to nutrients due to the periodic flooding, leading to faster growth.
- Oxygenation: The draining phase allows the roots to access oxygen, promoting healthy root development.
- Reduced water usage: It uses less water compared to other hydroponic systems, as the excess water is reused.
- Versatility: Suitable for various plant types, including vegetables, herbs, and flowering plants.
3. Disadvantages:
- System complexity: It can be more complex to set up compared to simpler hydroponic systems like Deep Water Culture (DWC).
- Equipment failure risk: If the pump or timer malfunctions, it can disrupt the flood and drain cycles and affect plant health.
- pH fluctuations: The constant cycling of water can lead to fluctuations in pH levels, requiring regular monitoring and adjustment.
Overall, the ebb and flow system can be an efficient and productive hydroponic method, but it requires careful maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal plant growth.